Java 异常
异常是程序运行过程中出现的错误或意外情况。Java 通过异常机制来处理运行时错误,使程序更加健壮。
异常架构
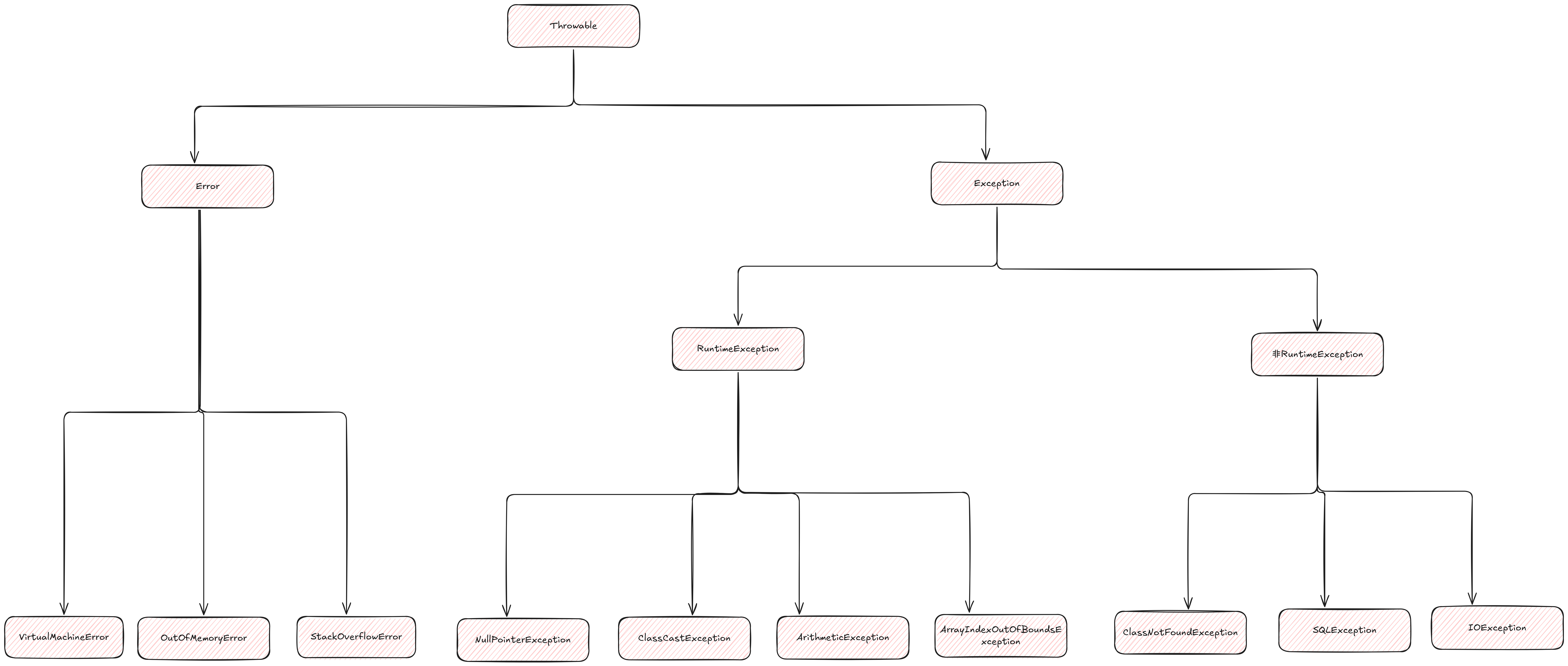
根据上面的异常架构, Java中的异常可以分为两大类:
- Error: 系统级错误,程序无法处理
- Exception: 程序可以处理的异常
- 受检异常(Checked Exception): 编译时必须处理
- 非受检异常(Unchecked Exception): 运行时异常,可以不处理
异常处理
try-catch-finally
java
try {
// 可能抛出异常的代码
int result = 10 / 0;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
// 处理算术异常
System.out.println("除数不能为0");
} catch (Exception e) {
// 处理其他异常
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 无论是否发生异常都会执行
// ...
}throw 和 throws
throw: 用于在方法内部抛出异常
java
public void checkAge(int age) {
if (age < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("年龄不能为负数");
}
}throws: 用于在方法签名中声明可能抛出的异常
java
public void readFile(String path) throws IOException {
FileReader reader = new FileReader(path);
// 读取文件操作
}try-with-resources
自动关闭资源, 仅适用于实现了 AutoCloseable 接口的类:
java
try (FileReader reader = new FileReader("file.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader)) {
String line = br.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 资源会自动关闭,无需finally块自定义异常
java
// 自定义受检异常
public class BusinessException extends Exception {
public BusinessException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
// 自定义非受检异常
public class CustomRuntimeException extends RuntimeException {
public CustomRuntimeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}参考实践
- 不要捕获 Throwable 或 Error
- 尽可能使用具体的异常类型
- 不要忽略异常 (避免空的catch块)
- 在合适的层级处理异常
- 记录异常信息,便于问题排查
- 优先使用标准异常
- 异常信息要清晰明确
- 及时释放资源,使用try-with-resources
